 Reading Time: 11 minutes read
Reading Time: 11 minutes read
Regression analysis is perhaps one of the most widely used statistical methods for investigating or estimating the relationship between a set of independent and dependent variables. In statistical analysis, distinguishing between categorical data and numerical data is essential, as categorical data involves distinct categories or labels, while numerical data consists of measurable quantities.
It is also used as a blanket term for various data analysis techniques utilized in a qualitative research method for modeling and analyzing numerous variables. In the regression method, the dependent variable is a predictor or an explanatory element, and the dependent variable is the outcome or a response to a specific query.
LEARN ABOUT: Statistical Analysis Methods
Definition of Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is often used to model or analyze data. Most survey analysts use it to understand the relationship between the variables, which can be further utilized to predict the precise outcome.
For Example – Suppose a soft drink company wants to expand its manufacturing unit to a newer location. Before moving forward, the company wants to analyze its revenue generation model and the various factors that might impact it. Hence, the company conducts an online survey with a specific questionnaire.
After using regression analysis, it becomes easier for the company to analyze the survey results and understand the relationship between different variables like electricity and revenue – here, revenue is the dependent variable.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
In addition, understanding the relationship between different independent variables like pricing, number of workers, and logistics with the revenue helps the company estimate the impact of varied factors on sales and profits.
Survey researchers often use this technique to examine and find a correlation between different variables of interest. It provides an opportunity to gauge the influence of different independent variables on a dependent variable.
Overall, regression analysis saves the survey researchers’ additional efforts in arranging several independent variables in tables and testing or calculating their effect on a dependent variable. Different types of analytical research methods are widely used to evaluate new business ideas and make informed decisions.
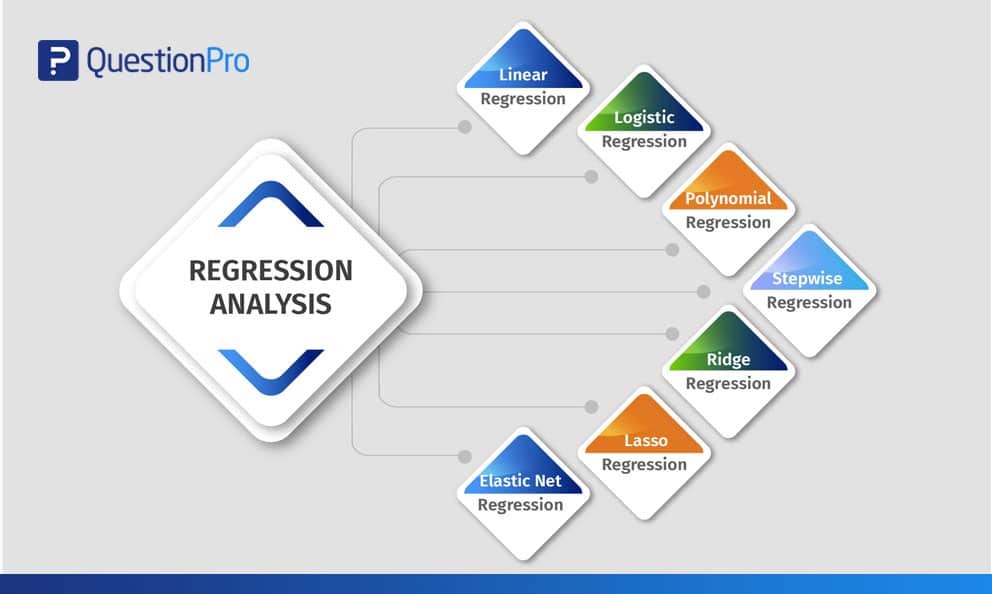
Types of Regression Analysis
Researchers usually start by learning linear and logistic regression first. Due to the widespread knowledge of these two methods and ease of application, many analysts think there are only two types of models. Each model has its own specialty and ability to perform if specific conditions are met.
This blog explains the commonly used seven types of multiple regression analysis methods that can be used to interpret the enumerated data in various formats.
01. Linear Regression Analysis
It is one of the most widely known modeling techniques, as it is amongst the first elite regression analysis methods picked up by people at the time of learning predictive modeling. Here, the dependent variable is continuous, and the independent variable is more often continuous or discreet with a linear regression line.
Please note that multiple linear regression has more than one independent variable than simple linear regression. Thus, linear regression is best to be used only when there is a linear relationship between the independent and a dependent variable.
Example
A business can use linear regression to measure the effectiveness of the marketing campaigns, pricing, and promotions on sales of a product. Suppose a company selling sports equipment wants to understand if the funds they have invested in the marketing and branding of their products have given them substantial returns or not.
Linear regression is the best statistical method to interpret the results. The best thing about linear regression is it also helps in analyzing the obscure impact of each marketing and branding activity, yet controlling the constituent’s potential to regulate the sales.
If the company is running two or more advertising campaigns simultaneously, one on television and two on radio, then linear regression can easily analyze the independent and combined influence of running these advertisements together.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Analytics Projects
02. Logistic Regression Analysis
Logistic regression is commonly used to determine the probability of event success and event failure. Logistic regression is used whenever the dependent variable is binary, like 0/1, True/False, or Yes/No. Thus, it can be said that logistic regression is used to analyze either the close-ended questions in a survey or the questions demanding numeric responses in a survey.
Please note logistic regression does not need a linear relationship between a dependent and an independent variable, just like linear regression. Logistic regression applies a non-linear log transformation for predicting the odds ratio; therefore, it easily handles various types of relationships between a dependent and an independent variable.
Example
Logistic regression is widely used to analyze categorical data, particularly for binary response data in business data modeling. More often, logistic regression is used when the dependent variable is categorical, like to predict whether the health claim made by a person is real(1) or fraudulent, to understand if the tumor is malignant(1) or not.
Businesses use logistic regression to predict whether the consumers in a particular demographic will purchase their product or will buy from the competitors based on age, income, gender, race, state of residence, previous purchase, etc.
03. Polynomial Regression Analysis
Polynomial regression is commonly used to analyze curvilinear data when an independent variable’s power is more than 1. In this regression analysis method, the best-fit line is never a ‘straight line’ but always a ‘curve line’ fitting into the data points.
Please note that polynomial regression is better to use when two or more variables have exponents and a few do not.
Additionally, it can model non-linearly separable data offering the liberty to choose the exact exponent for each variable, and that too with full control over the modeling features available.
Example
When combined with response surface analysis, polynomial regression is considered one of the sophisticated statistical methods commonly used in multisource feedback research. Polynomial regression is used mostly in finance and insurance-related industries where the relationship between dependent and independent variables is curvilinear.
Suppose a person wants to budget expense planning by determining how long it would take to earn a definitive sum. Polynomial regression, by taking into account his/her income and predicting expenses, can easily determine the precise time he/she needs to work to earn that specific sum amount.
04. Stepwise Regression Analysis
This is a semi-automated process with which a statistical model is built either by adding or removing the dependent variable on the t-statistics of their estimated coefficients.
If used properly, the stepwise regression will provide you with more powerful data at your fingertips than any method. It works well when you are working with a large number of independent variables. It just fine-tunes the unit of analysis model by poking variables randomly.
Stepwise regression analysis is recommended to be used when there are multiple independent variables, wherein the selection of independent variables is done automatically without human intervention.
Please note, in stepwise regression modeling, the variable is added or subtracted from the set of explanatory variables. The set of added or removed variables is chosen depending on the test statistics of the estimated coefficient.
Example
Suppose you have a set of independent variables like age, weight, body surface area, duration of hypertension, basal pulse, and stress index based on which you want to analyze its impact on the blood pressure.
In stepwise regression, the best subset of the independent variable is automatically chosen; it either starts by choosing no variable to proceed further (as it adds one variable at a time) or starts with all variables in the model and proceeds backward (removes one variable at a time).
Thus, using regression analysis, you can calculate the impact of each or a group of variables on blood pressure.
05. Ridge Regression Analysis
Ridge regression is based on an ordinary least square method which is used to analyze multicollinearity data (data where independent variables are highly correlated). Collinearity can be explained as a near-linear relationship between variables.
Whenever there is multicollinearity, the estimates of least squares will be unbiased, but if the difference between them is larger, then it may be far away from the true value. However, ridge regression eliminates the standard errors by appending some degree of bias to the regression estimates with a motive to provide more reliable estimates.
If you want, you can also learn about Selection Bias through our blog.
Please note, Assumptions derived through the ridge regression are similar to the least squared regression, the only difference being the normality. Although the value of the coefficient is constricted in the ridge regression, it never reaches zero suggesting the inability to select variables.
Example
Suppose you are crazy about two guitarists performing live at an event near you, and you go to watch their performance with a motive to find out who is a better guitarist. But when the performance starts, you notice that both are playing black-and-blue notes at the same time.
Is it possible to find out the best guitarist having the biggest impact on sound among them when they are both playing loud and fast? As both of them are playing different notes, it is substantially difficult to differentiate them, making it the best case of multicollinearity, which tends to increase the standard errors of the coefficients.
Ridge regression addresses multicollinearity in cases like these and includes bias or a shrinkage estimation to derive results.
06. Lasso Regression Analysis
Lasso (Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator) is similar to ridge regression; however, it uses an absolute value bias instead of the square bias used in ridge regression.
It was developed way back in 1989 as an alternative to the traditional least-squares estimate with the intention to deduce the majority of problems related to overfitting when the data has a large number of independent variables.
Lasso has the capability to perform both – selecting variables and regularizing them along with a soft threshold. Applying lasso regression makes it easier to derive a subset of predictors from minimizing prediction errors while analyzing a quantitative response.
Please note that regression coefficients reaching zero value after shrinkage are excluded from the lasso model. On the contrary, regression coefficients having more value than zero are strongly associated with the response variables, wherein the explanatory variables can be either quantitative, categorical, or both.
Example
Suppose an automobile company wants to perform a research analysis on average fuel consumption by cars in the US. For samples, they chose 32 models of car and 10 features of automobile design – Number of cylinders, Displacement, Gross horsepower, Rear axle ratio, Weight, ¼ mile time, v/s engine, transmission, number of gears, and number of carburetors.
As you can see a correlation between the response variable mpg (miles per gallon) is extremely correlated to some variables like weight, displacement, number of cylinders, and horsepower. The problem can be analyzed by using the glmnet package in R and lasso regression for feature selection.
07. Elastic Net Regression Analysis
It is a mixture of ridge and lasso regression models trained with L1 and L2 norms. The elastic net brings about a grouping effect wherein strongly correlated predictors tend to be in/out of the model together. Using the elastic net regression model is recommended when the number of predictors is far greater than the number of observations.
Please note that the elastic net regression model came into existence as an option to the lasso regression model as lasso’s variable section was too much dependent on data, making it unstable. By using elastic net regression, statisticians became capable of over-bridging the penalties of ridge and lasso regression only to get the best out of both models.
Example
A clinical research team having access to a microarray data set on leukemia (LEU) was interested in constructing a diagnostic rule based on the expression level of presented gene samples for predicting the type of leukemia. The data set they had, consisted of a large number of genes and a few samples.
Apart from that, they were given a specific set of samples to be used as training samples, out of which some were infected with type 1 leukemia (acute lymphoblastic leukemia) and some with type 2 leukemia (acute myeloid leukemia).
Model fitting and tuning parameter selection by tenfold CV were carried out on the training data. Then they compared the performance of those methods by computing their prediction mean-squared error on the test data to get the necessary results.
Regression analysis usage in market research
A market research survey focuses on three major matrices; Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty, and Customer Advocacy. Remember, although these matrices tell us about customer health and intentions, they fail to tell us ways of improving the position. Therefore, an in-depth survey questionnaire intended to ask consumers the reason behind their dissatisfaction is definitely a way to gain practical insights.
However, it has been found that people often struggle to put forth their motivation or demotivation or describe their satisfaction or dissatisfaction. In addition to that, people always give undue importance to some rational factors, such as price, packaging, etc. Overall, it acts as a predictive analytic and forecasting tool in market research.
When used as a forecasting tool, regression analysis can determine an organization’s sales figures by taking into account external market data. A multinational company conducts a market research survey to understand the impact of various factors such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), CPI (Consumer Price Index), and other similar factors on its revenue generation model.
Obviously, regression analysis in consideration of forecasted marketing indicators was used to predict a tentative revenue that will be generated in future quarters and even in future years. However, the more forward you go in the future, the data will become more unreliable, leaving a wide margin of error.
Case study of using regression analysis
A water purifier company wanted to understand the factors leading to brand favorability. The survey was the best medium for reaching out to existing and prospective customers. A large-scale consumer survey was planned, and a discreet questionnaire was prepared using the best survey tool.
A number of questions related to the brand, favorability, satisfaction, and probable dissatisfaction were effectively asked in the survey. After getting optimum responses to the survey, regression analysis was used to narrow down the top ten factors responsible for driving brand favorability.
All the ten attributes derived (mentioned in the image below) in one or the other way highlighted their importance in impacting the favorability of that specific water purifier brand.

How regression analysis derives insights from surveys?
It is easy to run a regression analysis using Excel or SPSS, but while doing so, the importance of four numbers in interpreting the data must be understood.
The first two numbers out of the four numbers directly relate to the regression model itself.
- F-Value: It helps in measuring the statistical significance of the survey model. Remember, an F-Value significantly less than 0.05 is considered to be more meaningful. Less than 0.05 F-Value ensures survey analysis output is not by chance.
- R-Squared: This is the value wherein the independent variables try to explain the amount of movement by dependent variables. Considering the R-Squared value is 0.7, a tested independent variable can explain 70% of the dependent variable’s movement. It means the survey analysis output we will be getting is highly predictive in nature and can be considered accurate.
The other two numbers relate to each of the independent variables while interpreting regression analysis.
- P-Value: Like F-Value, even the P-Value is statistically significant. Moreover, here it indicates how relevant and statistically significant the independent variable’s effect is. Once again, we are looking for a value of less than 0.05.
- Interpretation: The fourth number relates to the coefficient achieved after measuring the impact of variables. For instance, we test multiple independent variables to get a coefficient. It tells us, ‘by what value the dependent variable is expected to increase when independent variables (which we are considering) increase by one when all other independent variables are stagnant at the same value.
In a few cases, the simple coefficient is replaced by a standardized coefficient demonstrating the contribution from each independent variable to move or bring about a change in the dependent variable.
Advantages of using regression analysis in an online survey
01. Get access to predictive analytics
Do you know utilizing regression analysis to understand the outcome of a business survey is like having the power to unveil future opportunities and risks?
For example, after seeing a particular television advertisement slot, we can predict the exact number of businesses using that data to estimate a maximum bid for that slot. The finance and insurance industry as a whole depends a lot on regression analysis of survey data to identify trends and opportunities for more accurate planning and decision-making.
02. Enhance operational efficiency
Do you know businesses use regression analysis to optimize their business processes?
For example, before launching a new product line, businesses conduct consumer surveys to better understand the impact of various factors on the product’s production, packaging, distribution, and consumption.
A data-driven foresight helps eliminate the guesswork, hypothesis, and internal politics from decision-making. A deeper understanding of the areas impacting operational efficiencies and revenues leads to better business optimization.
03. Quantitative support for decision-making
Business surveys today generate a lot of data related to finance, revenue, operation, purchases, etc., and business owners are heavily dependent on various data analysis models to make informed business decisions.
For example, regression analysis helps enterprises to make informed strategic workforce decisions. Conducting and interpreting the outcome of employee surveys like Employee Engagement Surveys, Employee Satisfaction Surveys, Employer Improvement Surveys, Employee Exit Surveys, etc., boosts the understanding of the relationship between employees and the enterprise.
It also helps get a fair idea of certain issues impacting the organization’s working culture, working environment, and productivity. Furthermore, intelligent business-oriented interpretations reduce the huge pile of raw data into actionable information to make a more informed decision.
04. Prevent mistakes from happening due to intuitions
By knowing how to use regression analysis for interpreting survey results, one can easily provide factual support to management for making informed decisions. ; but do you know that it also helps in keeping out faults in the judgment?
For example, a mall manager thinks if he extends the closing time of the mall, then it will result in more sales. Regression analysis contradicts the belief that predicting increased revenue due to increased sales won’t support the increased operating expenses arising from longer working hours.
Conclusion
Regression analysis is a useful statistical method for modeling and comprehending the relationships between variables. It provides numerous advantages to various data types and interactions. Researchers and analysts may gain useful insights into the factors influencing a dependent variable and use the results to make informed decisions.
With QuestionPro Research, you can improve the efficiency and accuracy of regression analysis by streamlining the data gathering, analysis, and reporting processes. The platform’s user-friendly interface and wide range of features make it a valuable tool for researchers and analysts conducting regression analysis as part of their research projects.
Sign up for the free trial today and let your research dreams fly!









